Biomedical Informatics Qualify@YM
Common Rules 醫資資格考的通則 :
- 參考書籍 Biomedical Informatics: Computer Applications in Health Care and Biomedicine by Shortliffe and Comino
- 範圍建議可以指定重要的章節,公布學生參考.
- 考題出法,建議醫資兩人出
- 簡單4
- 適中2
- 深度2
- 然後隨機抽出簡單4題,適中2題,複雜1題,供學生考試使用.
Bible Chapters :
- Biomedical Informatics: The Science and the Pragmatics
- Biomedical Data: Their Acquisition, Storage, and Use
- Biomedical Decision Making: Probabilistic Clinical Reasoning
- Cognitive Science and Biomedical Informatics
- Computer Architectures for Health Care and Biomedicine
- Software Engineering for Health Care and Biomedicine
- Standards in Biomedical Informatics
- Natural Language Processing in Health Care and Biomedicine
- Biomedical Imaging Informatics
- Ethics in Biomedical and Health Informatics: Users, Standards, and Outcomes
- Evaluation of Biomedical and Health Information Resources
- Electronic Health Record Systems
- Health Information Infrastructure
- Management of Information in Health Care Organizations
- Patient-Centered Care Systems
- Public Health Informatics
- Consumer Health Informatics and Personal Health Records
- Telehealth
- Patient Monitoring Systems
- Imaging System in Radiology
- Information Retrieval and Digital Libraries
- Clinical Decision-Support Systems
- Computers in Health Care Education
- Bioinformatics
- Translational Bioinformatics
- Clinical Research Infromatics
- Health Information Technology Policy
- The Future of Informatics in Biomedicine
For Exam :
Biomedical Informatics: The Science and the Pragmatics- Biomedical Data: Their Acquisition, Storage, and Use (10% 40/300) 201412.2 | 201412.3 | 201412.4 | 201405.1 |
- Biomedical Decision Making: Probabilistic Clinical Reasoning (8.75% 35/300) 201405.2 | 201312.4 | 201312.5 |
- Cognitive Science and Biomedical Informatics
- Computer Architectures for Health Care and Biomedicine
- Software Engineering for Health Care and Biomedicine (15% 60/400) 201412.7 | 201405.5 | 201312.3 | 201605.2 |
- Standards in Biomedical Informatics (15% 60/400) 201412.8 | 201405.3 | 201405.4 | 201312.1 | 201605.1 |
- Natural Language Processing in Health Care and Biomedicine
- Biomedical Imaging Informatics (8.75% 35/400) 201412.6 | 201312.2 | 201605.3 |
- Ethics in Biomedical and Health Informatics: Users, Standards, and Outcomes
- Evaluation of Biomedical and Health Information Resources
- Electronic Health Record Systems (8.75% 35/400) 201412.1 | 201605.4 |
- Health Information Infrastructure
- Management of Information in Health Care Organizations
- Patient-Centered Care Systems
- Public Health Informatics
- Consumer Health Informatics and Personal Health Records
- Telehealth (3.75% 15/400) 201605.4 |
- Patient Monitoring Systems
- Imaging System in Radiology
- Information Retrieval and Digital Libraries
- Clinical Decision-Support Systems (10% 40/400) 201312.6 | 201312.7 |
- Computers in Health Care Education
- Bioinformatics
- Translational Bioinformatics
- Clinical Research Infromatics
- Health Information Technology Policy
- The Future of Informatics in Biomedicine (17.5% 70/400) 201405.6 | 201605.5 |
- Others (3.33% 10/300) 201412.5 |
201605
Hint from 張: Open Question like 201405.6, Topic include:
- Wearable Device & Applications
- Health Care Standards & Applications
- Please answer the following question. (20%, 劉)
- a. What is the data-interchange standard DICOM? (201312.1 考古)
- b. What is the data-interchange standard IEEE11073? (201312.1 考古)
- c. What is the Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG)? (201405.4 考古)
- d. What is the Current Procedure Terminology (CPT)? (201405.4 考古)
- Describe an outpatient clinic's billing system in terms of inputs, outputs, and processes. Sketch data-flow diagram, class diagram and sequence diagram that represents your model of the system. (15%, 劉) (201312.3 考古)
- What is segmentation step in image analysis? What is it so difficult to perform? Gave an example of how knowledge about the problem to be solved could be used in future system to aid automatic segmentation. (15%, 劉)
- 傳統的醫院信息系統(HIS), 電子醫令系統(CPOE), 和如今結合智慧型手機或穿戴式設備的行動健康系統(Molbile Health)的設計角度各自有什麼特色(15%)何不同(15%, 張).
- 為何臨床資訊應用的發展, 需要仰賴專業醫療人員的參與與設計? 請簡述四點理由(20%, 張)
201412
- 5 difference between physician & nurse use of information system (20%, 劉)
- Challenges of there differences in designing an "useful" ICT tool (10%, 劉)
- "Bigdata" in designing useful ICT tool for clinicans (10%, 劉)
- "Bigdata" in designing useful ICT tool for patients (10%, 劉)
- Identify all the referential expressions in the text below and determine the current referent for each. Assume computer attemps to identify referents by finding the most recent hour phrase. How well does this resolution rule work? Suggest a more effective rule. (10%, 劉)
- What additional informatics issue arise when going from 2D to 3D image processing? What are the 3D versions of 2D image processing operation such as region growing and edge detection? (10%, 劉)
- (20%, 劉)
- Explan the difference between outcome and process measures of system performance
- Identify two outcome and two process parameters that you might use to evaluate the performance of a clinical consultation system that assists physicians in diagnosing disease
- Describe an experiment that you could perform to evaluate the effect of the system on one of there parameters
- What potential difficulfie can you forces in conducting your experiment?
- What can you do to compensate for those difficulties
- Develop a regular expression to regularige the tokens in line 4-9 of the conclion catheterigation report show bellow (10%, 劉)
201412 Reference
6:
- The basic 2-D image processing operations of global processing, segmentation, feature detection, and classification generalize to higher dimensions.
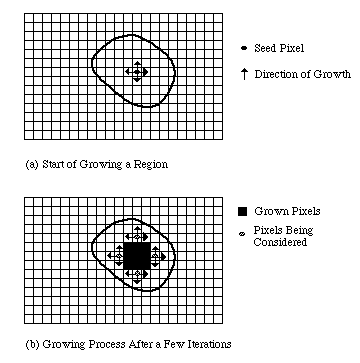
- Region Growing:

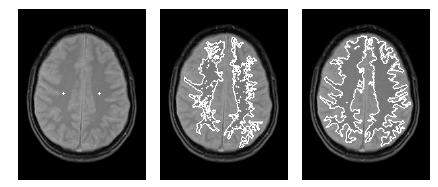
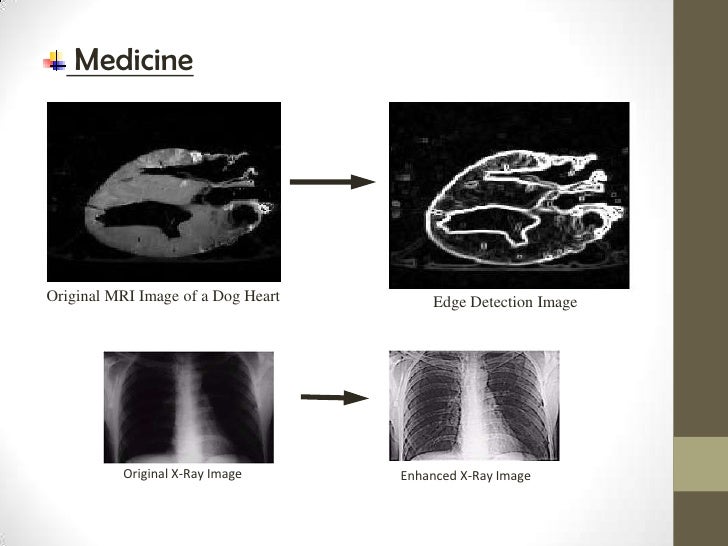
- Edge Detection
- 9.4.7 Image Registration
- 3-D and higher dimensionality images give rise to additional informatics issues, which include image registration, spatial representation of anatomy, symbolic representation of anatomy, integration of spatial and symbolic anatomic representations in atlases, anatomical variation, and characterization of anatomy.
- 9.4.6.1 Region-Based and Edge-Based Segmentation
- In the 2-D case, contour-following connects adjacent points on the boundary. In the 3-D case, isosurface-following or marching-cubes (Lorensen and Cline 1987 ) methods connect border voxels in a region into a 3-D surface mesh.
- 3D edge detection introduction
 8:
8:- Regular Expression Wiki
- Regular Expression Example
201405
- use of medical data (10%, 劉)
- performance of a test. What do they mean? 如何描述一個檢驗方法的好壞?(10%, 劉)
- 何謂編碼系統coding system?請舉一個例子說明?(10%, 劉)
- 何謂DRG,DRG跟CPT有和不同?(10%, 劉)
- Structured programming and object-oriented programming differences ? (10%, 劉)
- (50%, 張)
- 台灣跟其他國家相比,有哪些醫療資訊發展(topics of medical informatics)的機會(列出至少三項)
- 有哪些可以採取的策略(列出至少三項)
- 這些改變對臨床醫師
- 護理及其他醫療照護專業人員
- IT人員造成什麼影響?
201405 Reference
2:
4:
5:
201312
- Describe the following date-interchange standard : DICOM , HL7, IEEE11073 (10%, 劉)
- Describe Voxel registration and volume registration (10%, 劉)
- Describe an outpatient clinic billing system in term of inputs, outputs and processes. Sketch data-flow diagram , class diagram and sequence diagram that represents your model of the system (15%, 劉)
- What is post-test probability ? If prior possibility=0.9, sensitivity=0.9, specificity=0.8 , what is the post-test probability of patient having the disease if the test result is positive ? (15%, 張)
- What is the "sensitivity analysis" mean in a decision analysis problem? (10%, 張)
- What is the same ? (5%, 張) and difference ? (5%, 張) among information system of Decision support system and expert system ?
- From your own professional perspective, how could you design a system with the components of information system, decision support system and expert system to prevent medication errors? (30%, 張)
201312 Reference
1:
- LOINC , SNOMED CT , ICD , HIPPA ,
- DICOM ,
- HL7中文簡介 ,
- HL7 V2 , HL7 V3 , HL7 CDA R2 , HL7 FHIR ,
- IEEE11073 wiki , IEEE11073中文簡介 ,
- IHE ,
- Continua Alliance

2:
- 3-D volume array

- Bible 9.4.7 Image Registration
- 3-D image volume data are represented in the computer by a 3-D volume array, in which each voxel represents the image intensity in a small volume of space. In order to depict anatomy accurately, the voxels must be accurately registered (or located) in the 3-D volume ( voxel registration ), and separately acquired image volumes from the same subject must be registered with each other ( volume registration ).
- 9.4.7.1 Voxel Registration
- 9.4.7.2 Volume Registration
4&5: